Linked List: A Comprehensive Guide
Have you ever wondered what makes a linked list so special in the world of data structures? If you’re looking to dive deeper into this fascinating concept, you’ve come to the right place. In this article, we’ll explore the intricacies of linked lists from various angles, including their definition, types, implementation, and real-world applications. So, let’s get started!
What is a Linked List?
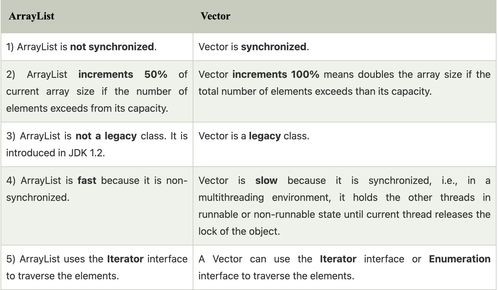
A linked list is a linear data structure that consists of a sequence of nodes. Each node contains two main components: data and a reference (or link) to the next node in the sequence. This structure allows for efficient insertion and deletion of elements, making it a popular choice in many programming scenarios.
Types of Linked Lists
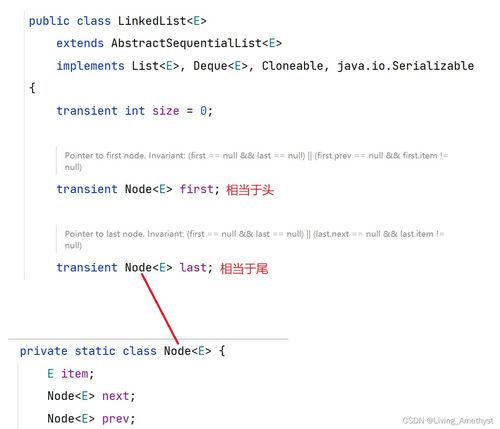
There are several types of linked lists, each with its unique characteristics and use cases. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common ones:
-
Singly Linked List
-
Doubly Linked List
-
Circular Linked List
-
Looped Linked List
-
Stack-Linked List
-
Queue-Linked List
Here’s a brief overview of each type:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Singly Linked List | Each node contains a data field and a reference to the next node in the sequence. |
| Doubly Linked List | Each node contains a data field and two references: one to the next node and one to the previous node. |
| Circular Linked List | The last node in the sequence points back to the first node, creating a circular structure. |
| Looped Linked List | Contains a cycle, where one or more nodes are repeated in the sequence. |
| Stack-Linked List | Utilizes a linked list to implement a stack data structure, with operations like push and pop. |
| Queue-Linked List | Utilizes a linked list to implement a queue data structure, with operations like enqueue and dequeue. |
Implementation of a Linked List
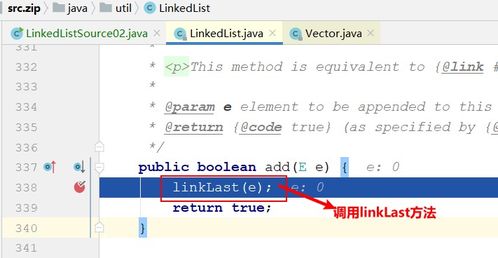
Implementing a linked list involves creating a node class and a linked list class. Let’s take a look at a simple implementation in Python:
class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = Noneclass LinkedList: def __init__(self): self.head = None def append(self, data): new_node = Node(data) if not self.head: self.head = new_node return last_node = self.head while last_node.next: last_node = last_node.next last_node.next = new_node def display(self): elements = [] current_node = self.head while current_node: elements.append(current_node.data) current_node = current_node.next return elements
Real-World Applications of Linked Lists
Linked lists are widely used in various applications due to their flexibility and efficiency. Here are some examples:
-
Database Management Systems
-
Operating Systems
-
Web Browsers
-
File Systems
-
Graph Algorithms
For instance, in a database management system, linked lists can be used to store and manage records efficiently. Similarly, in operating systems, linked lists are used to manage processes and memory allocation.
Conclusion
Linked lists are a powerful and versatile data structure that offers numerous benefits in various programming scenarios. By understanding the different types, implementation, and real-world applications of linked lists, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle a wide range of challenges in your programming journey. Happy coding







