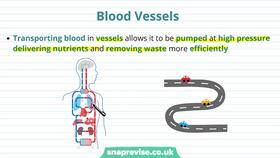
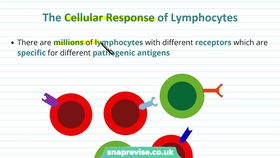
Link Reaction: A Comprehensive Overview
Have you ever wondered about the fascinating world of chemical reactions? One such reaction that has intrigued scientists and chemists alike is the link reaction. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of link reactions, exploring their definition, types, mechanisms, and applications. So, let’s embark on this journey of discovery and unravel the mysteries of link reactions.
What is a Link Reaction?

A link reaction, also known as a coupling reaction, is a chemical process where two or more molecules combine to form a single product. This reaction is characterized by the formation of a new bond between the reacting molecules, resulting in the creation of a larger molecule. Link reactions play a crucial role in various fields, including organic synthesis, polymer chemistry, and pharmaceuticals.
Types of Link Reactions
Link reactions can be categorized into several types based on the nature of the reacting molecules and the type of bond formed. Here are some common types of link reactions:
-
Diels-Alder Reaction: This reaction involves the formation of a cyclic compound from a diene and a dienophile.
-
Conjugate Addition: In this reaction, a nucleophile adds to an electrophilic double bond, resulting in the formation of a new bond.
-
Michael Addition: This reaction involves the addition of a nucleophile to an 伪,尾-unsaturated ketone or aldehyde.
-
Claisen Condensation: This reaction involves the condensation of two molecules, leading to the formation of a 尾-keto ester.
-
Perkin Reaction: This reaction involves the formation of a 尾-diketone from an aldehyde and an aromatic aldehyde.
Mechanism of Link Reactions
The mechanism of link reactions can vary depending on the specific reaction type. However, most link reactions follow a general mechanism involving the following steps:
-
Initiation: The reaction starts with the formation of reactive intermediates, such as radicals, carbocations, or carbanions.
-
Termination: The reaction ends when the reactive intermediates combine with each other or with other molecules, resulting in the formation of stable products.
Applications of Link Reactions
Link reactions have numerous applications in various fields. Here are some of the key applications:
-
Organic Synthesis: Link reactions are widely used in the synthesis of complex organic molecules, such as pharmaceuticals, natural products, and polymers.
-
Polymer Chemistry: Link reactions play a crucial role in the formation of polymers, which are used in various applications, including textiles, packaging, and construction materials.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Link reactions are employed in the synthesis of many drugs, including antibiotics, antivirals, and anticancer agents.
-
Biochemistry: Link reactions are involved in various biological processes, such as protein synthesis and DNA replication.
Table: Common Link Reactions and Their Applications
| Link Reaction | Application |
|---|---|
| Diels-Alder Reaction | Synthesis of cyclic compounds, natural products |
| Conjugate Addition | Synthesis of alkenes, esters, and amides |
| Michael Addition | Synthesis of 尾-keto esters, heterocycles |
| Claisen Condensation | Synthesis of 尾-keto esters, lactones |
| Perkin Reaction | Synthesis of 尾-diketones, dyes |
In conclusion, link reactions are fascinating chemical processes that play a vital role



















