Understanding Link Local IPv6 Address: A Comprehensive Guide
Link-local IPv6 addresses are an essential part of the IPv6 protocol, providing a unique way for devices to communicate on a local network without the need for a router or a global IP address. In this detailed guide, we will explore what link-local IPv6 addresses are, how they work, and their significance in modern networking.
What is a Link-Local IPv6 Address?
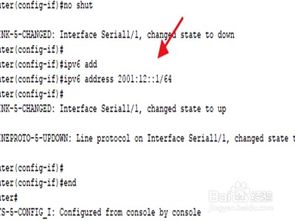
A link-local IPv6 address is a type of IPv6 address that is automatically assigned to a device when it joins a local network. These addresses are used for communication within the local network and are not routable on the internet. The format of a link-local IPv6 address is as follows:
fe80:%
Here,
How Does a Link-Local IPv6 Address Work?
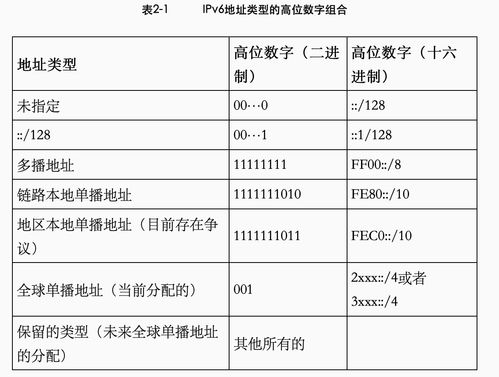
When a device joins a local network, it automatically generates a link-local IPv6 address using the following steps:
- The device selects a random interface identifier (interface-id) from a pool of available identifiers.
- The device combines the interface identifier with the link-local prefix (0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1) to form the link-local IPv6 address.
- The device then broadcasts this address on the local network, allowing other devices to discover and communicate with it.
This process is known as stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC), and it eliminates the need for manual address assignment or the use of a DHCP server.
Significance of Link-Local IPv6 Addresses
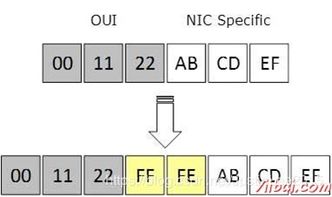
Link-local IPv6 addresses play a crucial role in modern networking for several reasons:
- Device Discovery: Link-local addresses enable devices to discover and communicate with each other on a local network without the need for a central server.
- Zero Configuration Networking: SLAAC allows devices to automatically configure their network settings, reducing the need for manual configuration or the use of a DHCP server.
- Scalability: Link-local addresses provide a scalable solution for small to medium-sized networks, as they eliminate the need for a DHCP server and reduce the complexity of network management.
- IPv6 Transition: Link-local addresses facilitate the transition from IPv4 to IPv6, as they allow devices to communicate using IPv6 even if the network infrastructure is still using IPv4.
Examples of Link-Local IPv6 Addresses
Here are some examples of link-local IPv6 addresses:
| Interface Identifier | Link-Local IPv6 Address |
|---|---|
| 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E | fe80::21a:2b3c:4d5e |
| 01:23:45:67:89:AB | fe80::123:4567:89ab |
| 02:34:56:78:9A:BC | fe80::234:5678:9abc |
Conclusion
Link-local IPv6 addresses are a vital component of modern networking, providing a simple and efficient way for devices to communicate on a local network. By understanding how link-local addresses work and their significance, you can better appreciate their role in the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 and the overall efficiency of modern networks.

















