Data Link Layer vs Network Addresses: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the differences between the data link layer and network addresses is crucial for anyone delving into the intricacies of computer networking. These two components play distinct roles in the communication process, and their proper functioning ensures seamless data transmission across networks. Let’s explore these concepts in detail, comparing their functionalities, purposes, and applications.
Data Link Layer
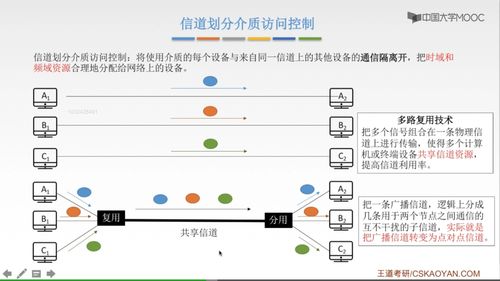
The data link layer is the second layer in the OSI model, responsible for the reliable transfer of data between adjacent network nodes. It operates at the local network level and ensures that data is transmitted error-free and efficiently. Here are some key aspects of the data link layer:
-
Frame Formation: The data link layer breaks the data received from the network layer into smaller, manageable units called frames. These frames contain control information, such as source and destination addresses, to facilitate error detection and correction.
-
Medium Access Control (MAC): The data link layer manages access to the shared communication medium, ensuring that multiple devices can communicate without interference. It uses MAC addresses to identify devices on the same network segment.
-
Flow Control: To prevent data loss and congestion, the data link layer implements flow control mechanisms. These mechanisms regulate the rate of data transmission between sender and receiver, ensuring that the receiver can handle the incoming data.
-
Error Detection and Correction: The data link layer incorporates error detection and correction techniques to ensure the integrity of the transmitted data. This includes checksums and cyclic redundancy checks (CRC) to identify and rectify errors.
Network Addresses

Network addresses, also known as IP addresses, are unique identifiers assigned to devices on a network. They enable devices to communicate with each other across different networks. Here are some essential aspects of network addresses:
-
IP Address Format: Network addresses are typically represented in a four-octet format, separated by dots. Each octet ranges from 0 to 255, representing a total of 4,294,967,296 unique addresses.
-
IPv4 vs IPv6: The current standard for network addresses is IPv4, which provides around 4.3 billion addresses. However, due to the rapid growth of the internet, IPv6 was introduced to accommodate the increasing number of devices. IPv6 uses an eight-octet format, offering a virtually limitless number of addresses.
-
Subnetting: To divide a large network into smaller, manageable segments, subnetting is employed. Subnetting allows for efficient allocation of IP addresses and enhances network security.
-
Network Address Translation (NAT): NAT is a technique used to map multiple private IP addresses to a single public IP address. This allows multiple devices within a private network to share a single public IP address, conserving the limited pool of public IP addresses.
Comparison: Data Link Layer vs Network Addresses
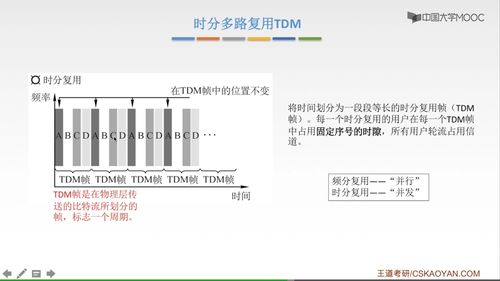
Now that we have a basic understanding of both the data link layer and network addresses, let’s compare them across various dimensions:
| Aspect | Data Link Layer | Network Addresses |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Ensures error-free and efficient data transfer between adjacent network nodes | Unique identifiers for devices on a network, enabling communication across different networks |
| Layer in OSI Model | Second layer | Third layer |
| Address Format | MAC addresses (6 octets) | IPv4 (4 octets) or IPv6 (8 octets) |
| Scope | Local network | Global network |
| Error Handling | Error detection and correction | Relies on higher layers for error handling |
While the data link layer and network addresses serve different purposes, they


















