x Linked Inheritance Diseases: A Detailed Overview
Understanding x-linked inheritance diseases is crucial for individuals, families, and healthcare professionals alike. These conditions affect both men and women, but their impact and presentation can vary significantly due to the unique nature of the X chromosome. Let’s delve into the intricacies of x-linked inheritance diseases, exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management.
What are X-Linked Inheritance Diseases?

X-linked inheritance refers to the pattern of inheritance of a trait or disorder that is determined by genes located on the X chromosome. Since males have one X and one Y chromosome, while females have two X chromosomes, the expression of x-linked traits can differ between genders. X-linked diseases can be dominant or recessive, and they can affect various aspects of health, from physical to cognitive functions.
Causes of X-Linked Inheritance Diseases
The primary cause of x-linked inheritance diseases is a mutation in the genes located on the X chromosome. These mutations can be inherited from either parent, and their impact can vary depending on the type of mutation and the individual’s sex. Some common causes include:
- Mutations in the X chromosome that lead to the production of a non-functional protein.
- Deletions or insertions of genetic material that alter the structure or function of the gene.
- Changes in the number of X chromosomes, such as Turner syndrome.
Types of X-Linked Inheritance Diseases
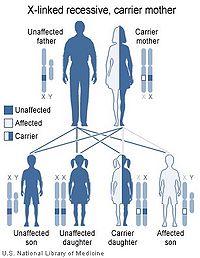
There are several types of x-linked inheritance diseases, each with its unique characteristics. Here are some of the most common ones:
- Color Blindness: A condition where an individual has difficulty distinguishing between certain colors. It is usually inherited in an x-linked recessive manner.
- Haemophilia A: A bleeding disorder caused by a deficiency in clotting factor VIII. It is an x-linked recessive disorder, more common in males.
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: A progressive muscle disorder that affects boys, usually starting in early childhood. It is an x-linked recessive disorder.
- Fragile X Syndrome: The most common inherited form of intellectual disability. It is an x-linked recessive disorder, affecting both males and females.
Symptoms of X-Linked Inheritance Diseases
The symptoms of x-linked inheritance diseases can vary widely, depending on the specific condition. Common symptoms include:
- Physical disabilities, such as muscle weakness or joint problems.
- Cognitive impairments, such as intellectual disability or learning difficulties.
- Reproductive issues, such as infertility or sexual development problems.
- Blood disorders, such as hemophilia or clotting factor deficiencies.
Diagnosis of X-Linked Inheritance Diseases
Diagnosing x-linked inheritance diseases often requires a combination of clinical evaluation, family history, and genetic testing. Some common diagnostic methods include:
- Physical examination to identify specific symptoms.
- Blood tests to measure levels of specific proteins or enzymes.
- Genetic testing to identify mutations in the affected genes.
Management and Treatment
The management and treatment of x-linked inheritance diseases depend on the specific condition and its severity. Some common approaches include:
- Supportive care, such as physical therapy or occupational therapy, to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Medications to manage specific symptoms, such as blood thinners for hemophilia or medications to improve cognitive function.
- Genetic counseling to help individuals and families understand the condition and its implications.
Prevention and Genetic Counseling
Preventing x-linked inheritance diseases involves understanding the risk factors and seeking genetic counseling. Genetic counseling can help individuals and families:
- Understand the risk of passing on the disorder to their children.
- Explore options for prenatal testing and screening.
- Learn about available treatments and support services.
In conclusion, x-linked inheritance diseases are a complex and diverse group of conditions that can have a significant impact on individuals and their families. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management of these diseases is crucial for effective care and support.

















