Understanding Recessive X-Linked Ichthyosis: A Comprehensive Guide
Recessive X-linked ichthyosis, often referred to as Recessive X-linked Ichthyosis (RXLI), is a rare genetic skin disorder that affects the skin’s ability to shed dead cells. This condition is characterized by thick, scaly skin, which can lead to discomfort and cosmetic concerns. In this article, we delve into the details of RXLI, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and the impact it has on individuals and their families.
What is Recessive X-Linked Ichthyosis?
RXLI is a genetic disorder caused by mutations in the ABCA12 gene, which is located on the X chromosome. This gene is responsible for producing a protein that helps in the shedding of skin cells. When the ABCA12 gene is mutated, the skin cells do not shed properly, leading to the thick, scaly skin that is characteristic of RXLI.
Causes and Genetics

The condition is inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern, which means that the gene mutation is located on the X chromosome. Males are more commonly affected by RXLI because they have only one X chromosome, while females have two. If a male inherits the mutated gene, he will have the disorder. Females, on the other hand, can be carriers of the gene mutation but may not exhibit symptoms unless they inherit the mutation from both parents.
Table 1: Inheritance Patterns of Recessive X-Linked Ichthyosis
| Genetic Makeup | Condition |
|---|---|
| XX | Carrier Female |
| XY | Affected Male |
| XX | Affected Female (rare) |
Symptoms
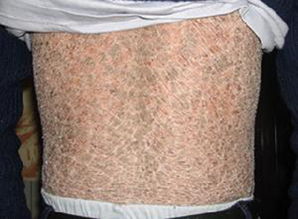
The symptoms of RXLI typically appear within the first few weeks of life. The most common symptom is the presence of thick, scaly skin, which can be found on the arms, legs, and trunk. The scales are often described as silvery or white and can be quite itchy. In some cases, the scales may also be found on the scalp, leading to hair loss.
Other symptoms may include:
- Severe dryness of the skin
- Cracking and bleeding of the skin
- Increased sensitivity to sunlight
- Discomfort and pain
Diagnosis
RXLI is typically diagnosed based on the appearance of the skin and a family history of the condition. A dermatologist may perform a skin biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. This involves taking a small sample of skin for examination under a microscope.
Treatment
There is no cure for RXLI, but there are several treatments that can help manage the symptoms. These include:
- Moisturizing creams and lotions to keep the skin hydrated
- Topical retinoids to help remove scales and improve skin texture
- Topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching
- Phototherapy, which involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of ultraviolet light
Impact on Individuals and Families
RXLI can have a significant impact on the lives of affected individuals and their families. The physical discomfort and cosmetic concerns associated with the condition can lead to social isolation and low self-esteem. However, with proper treatment and support, many individuals with RXLI are able to lead normal, fulfilling lives.
Support groups and counseling can also be beneficial for individuals and families affected by RXLI. These resources can provide information, emotional support, and practical advice for managing the condition.
Conclusion
RXLI is a rare genetic skin disorder that can have a significant impact on the lives of affected individuals and their families. Understanding the condition, its symptoms, and available treatments is crucial for managing the disorder effectively. With proper care and support, individuals with RXLI can lead healthy, happy lives.


















